Continual Us Involvement in Armed Conflicts
This is a list of wars and rebellions involving the United States of America. [1] Currently, there are 107 wars on this list, 3 of which are ongoing.
- USA defeat
- USA victory
- Another result (e.g. a treaty or peace without a clear result, status quo ante bellum, result of civil or internal conflict, result unknown or indecisive)
- Ongoing conflict
18th-century wars
| Conflict | Allies | Belligerent | Result for the United States and its Allies | Presidents of the United States |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| American Revolutionary War (1775–1783) Location: Eastern North America, Southern North America the Atlantic The Battle of Long Island, August 27, 1776 |
Watauga Association |
| US-allied victory
| President of the Continental Congress in American Revolutionary War:
|
| Cherokee–American wars (1776–1795) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: Old Southwest Abduction of Daniel Boone's daughter by the Cherokee | | | US-allied victory | President of the Continental Congress in Cherokee–American wars:
Presidents of the United States:
|
| Northwest Indian War (1785–1793) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: Northwest Territory The Battle of Fallen Timbers | | Western Confederacy List
| US-allied victory
| George Washington |
| Quasi-War (1798–1800) 'Location: Atlantic Ocean, the Caribbean, the Indian Ocean and the Mediterranean USS Constellation vs. L'Insurgente | Co-belligerent: |
| Convention of 1800
| John Adams |
19th-century wars
| Conflict | Allies | Belligerent | Result for the United States and its Allies | Presidents of the United States |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Barbary War (1801–1805) Part of the Barbary Wars Location: Mediterranean Sea off the coast of Tripoli Lieutenant Presley O'Bannon at Derna, April 1805 | | | US-allied victory | Thomas Jefferson |
| Tecumseh's War (1810–1813) Part of the American Indian Wars and the War of 1812 Location: Northwest River Ohio The Battle of Tippecanoe | | Tecumseh's Confederacy List
| US victory | James Madison |
| War of 1812 (1812–1815) Location: Eastern and Central North America General Andrew Jackson stands on the parapet of his makeshift defenses as his troops repulse attacking Highlanders, by painter Edward Percy Moran in 1910. | Creek Allies |
Tecumseh's Confederacy List
| Inconclusive/Other Result
| |
| Creek War (1813–1814) Part of the American Indian Wars and the War of 1812 Location: Southern United States The Battle of Horseshoe Bend, 1814 | Lower Creeks | Red Stick Creek | US-allied victory
| |
| Second Barbary War (1815) Part of the Barbary Wars Location: Mediterranean Sea and the Barbary States Decatur's squadron off Algiers | | | US victory | |
| First Seminole War (1817–1818) Part of the Seminole Wars and the American Indian Wars Location: Pensacola, Spanish Florida Barracks and tents at Fort Brooke near Tampa Bay | | Seminole | US victory
| James Monroe |
| Arikara War (1823) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: Missouri River An Arikara warrior | Sioux | Arikara | Inconclusive/Other Result
| |
| Winnebago War (1827) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: Illinois and Michigan Territory | | Prairie La Crosse Ho-Chunks with a few allies | US-allied victory
| John Quincy Adams |
| Black Hawk War (1832) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: Illinois and Michigan Territory Native women and children fleeing the Battle of Bad Axe | Ho-Chunk Menominee Potawatomi | Black Hawk's British Band Ho-Chunk and Potawatomi allies | US-allied victory
| Andrew Jackson |
| Texas Revolution (1835–1836) Location: Texas Fall of the Alamo |
| | Texan victory
| |
| Second Seminole War (1835–1842) Part of the Seminole Wars and the American Indian Wars Location: Florida, United States U.S. Marines search for Seminoles in the Everglades | | Seminole | US victory
| Martin Van Buren (March 4, 1837 – March 4, 1841) William Henry Harrison(March 4, 1841 – April 4, 1841) John Tyler (April 4, 1841 –March 4, 1845) |
| Comanche Wars (1836–1875) Part of the Texas–Indian wars and the American Indian Wars Location: South-central United States (Texas, Oklahoma, New Mexico, Kansas, Colorado) and northern Mexico U.S. Marines search for Seminoles in the Everglades | | | US victory | |
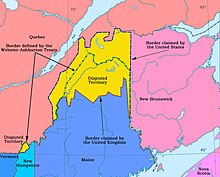
| Aroostook War (1838–1839) Location: Maine–New Brunswick border Map showing the boundary claims and final border | | | Inconclusive/Other Result
| Martin Van Buren |
| Mexican–American War (1846–1848) Location: Texas, New Mexico, California and Mexico 2nd Dragoons charge the enemy at the Battle of Resaca de la Palma, 1846 | | | US-allied victory
| James K. Polk |
| Cayuse War (1847–1855) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: Oregon The Whitman Massacre. | | Cayuse | US victory
| James K. Polk (March 4, 1845 – March 4, 1849) Zachary Taylor (March 4, 1849 – July 9, 1850) Millard Fillmore (July 9, 1850 – March 4, 1853) Franklin Pierce (March 4, 1853 – March 4, 1857) |
| Apache Wars (1849–1924) Part of the Texas–Indian wars and the American Indian Wars Location: Southwestern United States U.S. Cavalry dash for cover while fighting Apaches, by F. Remington | | Apache Ute Yavapai | US victory
| James K. Polk (March 4, 1845 – March 4, 1849) Zachary Taylor (March 4, 1849 – July 9, 1850) Millard Fillmore (July 9, 1850 – March 4, 1853) Franklin Pierce (March 4, 1853 – March 4, 1857) James Buchanan (March 4, 1857 – March 4, 1861) Abraham Lincoln (March 4, 1861 – April 15, 1865) Andrew Johnson (April 15, 1865 – March 4, 1869) Ulysses S. Grant (March 4, 1869 – March 4, 1877) Rutherford B. Hayes (March 4, 1877 – March 4, 1881) James A. Garfield (March 4, 1881 – September 19, 1881) Chester A. Arthur (September 19, 1881 – March 4, 1885) Grover Cleveland (March 4, 1885 – March 4, 1889) Benjamin Harrison (March 4, 1889 – March 4, 1893) Grover Cleveland (March 4, 1893 – March 4, 1897) William McKinley (March 4, 1897 – September 14, 1901) Theodore Roosevelt (September 14, 1901 – March 4, 1909) William Howard Taft (March 4, 1909 – March 4, 1913) Woodrow Wilson (March 4, 1913 – March 4, 1921) Warren G. Harding (March 4, 1921 – August 2, 1923) Calvin Coolidge (August 2, 1923 – March 4, 1929) |
| Navajo Wars (1849–1866) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: New Mexico Fort Defiance | | | US victory
| James K. Polk (March 4, 1845 – March 4, 1849) Zachary Taylor (March 4, 1849 – July 9, 1850) Millard Fillmore (July 9, 1850 – March 4, 1853) Franklin Pierce (March 4, 1853 – March 4, 1857) James Buchanan (March 4, 1857 – March 4, 1861) Abraham Lincoln (March 4, 1861 – April 15, 1865) Andrew Johnson (April 15, 1865 – March 4, 1869) |
| Bleeding Kansas (1854–1861) Location: Kansas and Missouri Sacking of Lawrence in 1856 | Anti-slavery settlers (Free-Staters) | Pro-slavery settlers (Border Ruffians) | Free-Stater victory.
| Franklin Pierce (March 4, 1853 – March 4, 1857) James Buchanan (March 4, 1857 – March 4, 1861) |
| Puget Sound War (1855–1856) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: Washington | Snoqualmie | Nisqually Muckleshoot Puyallup Klickitat Haida Tlingit | US victory
| Franklin Pierce |
| Rogue River Wars (1855–1856) Location: Rogue Valley | | Rogue River people | US victory
| |
| Third Seminole War (1855–1858) Part of the Seminole Wars and the American Indian Wars Location: Pensacola, Florida | | Seminole | US victory
| Franklin Pierce (March 4, 1853 – March 4, 1857) James Buchanan (March 4, 1857 – March 4, 1861) Abraham Lincoln (March 4, 1861 – April 15, 1865) Andrew Johnson (April 15, 1865 – March 4, 1869) |
| Yakima War (1855–1858) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: Washington Territory Seattleites evacuate to the town blockhouse as USSDecatur opens fire on advancing tribal forces. | Snoqualmie | Yakama Walla Walla tribe Umatilla tribe Nez Perce tribe Cayuse tribe | US victory | |
| Second Opium War (1856–1859) Part of the Opium Wars Location: China Palikao's bridge, on the evening of the battle, by Émile Bayard | | | US victory
| |
| Utah War (1857–1858) Part of the Mormon wars Location: Utah Territory and Wyoming | | Deseret/Utah Mormons (Nauvoo Legion) | Inconclusive/Other Result
| |
| Reform War (1858–1866) Location: Mexico | | | Liberals - US victory | |
| Pig War (1859) Location: San Juan Islands Proposed boundaries: Through Haro Strait, favored by the US Through Rosario Strait, favored by Britain Through San Juan Channel, compromise proposal The lines are as shown on maps of the time. The modern boundary follows straight line segments and roughly follows the blue line. The modern eastern boundary of San Juan County roughly follows the red line. |
|
| Inconclusive
| James Buchanan |
| John Brown's Raid on Harpers Ferry (1859) Part of pre-Civil War conflicts Location: West Virginia Harper's Weekly illustration of U.S. Marines attacking John Brown's "Fort" Teresa Baine | | Abolitionist Insurgents | US victory | |
| First and Second Cortina War (1859–1861) Location: Texas and Mexico | | | US-allied victory | |
| Paiute War (1860) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: Pyramid Lake, Nevada | | Paiute Shoshone Bannock | US victory | |
| American Civil War (1861–1865) Location: Southern United States, Indian Territory, Northeastern United States, Western United States, Atlantic Ocean The Battle of Antietam, by Thure de Thulstrup. | Indian Home Guard | Catawba | US victory
| Abraham Lincoln |
| Yavapai Wars (1861–1875) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: Arizona Rescue of Lt. Charles King | | Yavapai Apache Yuma Mohave | US victory | Abraham Lincoln (March 4, 1861 – April 15, 1865) Andrew Johnson (April 15, 1865 – March 4, 1869) Ulysses S. Grant (March 4, 1869 – March 4, 1877) |
| Dakota War of 1862 (1862) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: Minnesota and Dakota The Siege of New Ulm, Minnesota on August 19, 1862 | | | US victory | Abraham Lincoln |
| Colorado War (1863–1865) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: Colorado, Wyoming, and Nebraska | | | Inconclusive/Other Result
| |
| Snake War (1864–1868) Part of the American Indian Wars Locations: Oregon, Nevada, California, and Idaho | | Paiute Bannock Shoshone | US victory | Abraham Lincoln (March 4, 1861 – April 15, 1865) Andrew Johnson (April 15, 1865 – March 4, 1869) |
| Powder River War (1865) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: Powder River State | | | Inconclusive | Andrew Johnson |
| Red Cloud's War (1866–1868) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: Powder River State The Fetterman Massacre | | | Lakota-allied victory
| |
| Formosa Expedition (1867) Location: Hengchun, Taiwan, Qing China' Attack of United States Marines and Sailors on the pirates of the island of Formosa, East Indies, Harper's Weekly | | Paiwan | US victory | |
| Comanche Campaign (1867–1875) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: Western United States Battle of Beecher Island. One soldier and three horses have fallen, while others continue to wage the battle. | | Kiowa | US victory | Andrew Johnson (April 15, 1865 – March 4, 1869) Ulysses S. Grant (March 4, 1869 – March 4, 1877) |
| United States expedition to Korea (1871) Location: Ganghwa Island The captured Sujagi aboard USS Colorado in June 1871 | | | Inconclusive/Other Result American military victory American diplomatic failure
| Ulysses S. Grant |
| Modoc War (1872–1873) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: California and Oregon Engraving of soldiers recovering the bodies of the slain May 3, 1873. | | | US victory | |
| Red River War (1874–1875) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: Texas | | Kiowa | US victory
| |
| Las Cuevas War (1875) Location: Texas and Mexico Texan soldiers. | | Mexican bandits | US victory
| |
| Great Sioux War of 1876 (1876–1877) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: Montana, Dakota and Wyoming Custer's last stand at Little Bighorn. | | | US victory
| |
| Buffalo Hunters' War (1876–1877) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: Texas and Oklahoma | | Apache | US victory | |
| Nez Perce War (1877) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: Oregon, Idaho, Wyoming, and Montana Chief Joseph's band in the Battle of Bear Paw Mountain | | Nez Perce Palouse | US victory | Rutherford B. Hayes |
| Bannock War (1878) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: Idaho, Oregon, and Wyoming | | Bannock Shoshone Paiute | US victory | |
| Cheyenne War (1878–1879) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: Oklahoma, Kansas, Nebraska, South Dakota and Montana Aftermath of the Battle of "The Pit." | | | US victory | |
| Sheepeater Indian War (1879) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: Idaho | | Shoshone | US victory | |
| Victorio's War (1879–1880) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: Mexico | | Apache | US-allied victory | |
| White River War (1879) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: Colorado Battle of Milk Creek Canyon | | Ute | US victory | |
| Egyptian Expedition (1882) Part of the Anglo-Egyptian War Location: Alexandria Front page of "Judge" magazine, 12 August 1882, featuring a cartoon by "JAW" concerning aid rendered by the American navy during the British bombardment of Alexandria. | | | US victory | Grover Cleveland |
| Crow War (1887) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: Montana Crow Indians Firing into the Agency 1887 | | | US victory | |
| Ghost Dance War (1890–1891) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: South Dakota Mass grave for the dead Lakota after the conflict at Wounded Knee Creek. | | | US victory | Benjamin Harrison |
| Bering Sea Anti-Poaching Operations (1891) Location: Bering Sea, Pacific Ocean "Old Salts of the Square-Rigger Navy" on board USS Mohican, 1888, by H. W. Whitaker. | | Canadian Poachers | Anglo-American victory | |
| Garza War (1891–1893) Location: Texas and Mexico 3rd Cavalry Troopers searching a suspected Revolutionist, 1892 | | Garzistas | US-allied victory | |
| Yaqui Wars (1896–1918) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: Arizona and Mexico 10th Cavalry soldiers holding Yaqui prisoners at their camp in Bear Valley, January 9, 1918. | | Pima Opata | US-allied victory | Grover Cleveland (March 4, 1893 – March 4, 1897) |
| Second Samoan Civil War (1898–1899) Location: Samoa Samoan warriors and American servicemen during the Siege of Apia in March 1899. | Samoa | Mataafans | Inconclusive/Other Result
| William McKinley |
| Spanish–American War (1898) Location: Cuba, Puerto Rico, Philippines and Guam Theodore Roosevelt and the "Rough Riders" after the Battle of San Juan Hill. | |
| US-allied victory
| |
| Philippine–American War (1899–1902) Location: Philippines U.S. soldiers during the Battle of Manila. | 1899–1902
1902-1906
| 1899–1902
Limited Foreign Support:
1902-1906
| US victory
| William McKinley (March 4, 1897 – September 14, 1901) |
| Moro Rebellion (1899–1913) Location: Philippines American soldiers battling against Moro fighters. | | | US victory
| William McKinley (March 4, 1897 – September 14, 1901) |
| Boxer Rebellion (1899–1901) Location: China U.S. soldiers during the Boxer Rebellion in China. |
| | US-allied victory
| William McKinley |
20th-century wars
| Conflict | Allies | Belligerent | Result for the United States and its Allies | Presidents of the United States |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crazy Snake's War (1909) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: Oklahoma Creek prisoners of war. | | Creek | US victory | Theodore Roosevelt (September 14, 1901 – March 4, 1909) Warren G. Harding Calvin Coolidge |
| Mexican Border War (1910–1919) Part of the Mexican Revolution Location: Mexico–United States border American troops of the 16th Infantry Regiment rest for the night on May 27, 1916 | | Supported by:
| US victory
| William Howard Taft (March 4, 1909 – March 4, 1913) Woodrow Wilson |
| Little Race War (1912) Part of the Banana Wars Location: Cuba USS Mississippi in Cuba | | | US-allied victory
| William Howard Taft |
| United States occupation of Nicaragua (1912–1933) Part of the Banana Wars Location: Nicaragua US Marines holding a captured Sandinista flag. | | | US victory
| William Howard Taft (March 4, 1909 – March 4, 1913) Woodrow Wilson Warren G. Harding Calvin Coolidge Herbert Hoover |
| Bluff War (1914–1915) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: Utah and Colorado Prisoners of the Bluff War in Thompson, Utah, waiting to board a train for their trial in Salt Lake City. | | Ute Paiute | US victory | Woodrow Wilson |
| United States occupation of Veracruz (1914) Part of the Mexican Revolution Location: Mexico American ships at Veracruz | Supported by:
| Supported by:
| US victory | |
| United States occupation of Haiti (1915–1934) Part of the Banana Wars Location: Haiti 2nd Marine Regiment in Haiti | | | US-allied victory | Woodrow Wilson (March 4, 1913 – March 4, 1921) Warren G. Harding Calvin Coolidge Herbert Hoover Franklin D. Roosevelt |
| United States occupation of the Dominican Republic (1916–1924) Part of the Banana Wars Location: Dominican Republic US Marines in the Occupation of the Dominican Republic. | | | US victory | Woodrow Wilson (March 4, 1913 – March 4, 1921) Warren G. Harding Calvin Coolidge |
| World War I (1917–1918) Location: Europe, Africa, Asia, Middle East, the Pacific Islands, and coast of North and South America US troops firing 37mm gun during an advance against German entrenched positions. |
| | US-allied victory
| Woodrow Wilson |
| Russian Civil War (1918–1920) Location: Russia, Mongolia, and Iran US troops march through Russia before the Battle of Romanovka. |
| | Bolshevik victory
| |
| Posey War (1923) Part of the American Indian Wars Location: Utah Ute and Paiute prisoners of war. | | Ute Paiute | US victory
| Warren G. Harding |
| World War II (1941–1945) Location: Europe, Pacific Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, Southeast Asia, East Asia, Middle East, Mediterranean, North Africa, Oceania, North and South America Six United States Marines raising the U.S. flag atop Mount Suribachi during the Battle of Iwo Jima. |
| | US-allied victory
| Franklin D. Roosevelt Harry S. Truman |
| Korean War (1950–1953) Part of the Cold War Location: Korea U.S. soldier fires a 75mm recoilless rifle, near Oetlook-tong, Korea, in support of infantry units directly across the valley. | |
| Inconclusive/Other Result
| Harry S. Truman (April 12, 1945 – January 20, 1953) Dwight D. Eisenhower |
| Vietnam War (1955–1964[a], 1965–1973[b], 1974–1975[c]) Part of the Cold War and Indochina Wars Location: Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos 1st Cavalry Division, Battle of Ia Drang, 1965. | | Supported by:
| North Vietnam-allied victory
| Dwight D. Eisenhower (January 20, 1953 – January 20, 1961) John F. Kennedy Lyndon B. Johnson Richard Nixon Gerald Ford |
| Laotian Civil War (1959–1975) Part of the Indochina Wars and Cold War Location: Laos A U.S. Air Force Bell UH-1P from the 20th Special Operations Squadron "Green Hornets" at a base in Laos, 1970. | Supported by: | Supported by:
| Pathet Lao-allied victory
| |
| Lebanon crisis (1958) Location: Lebanon US Marine sits in a foxhole and points his machine gun toward Beirut. | |
| US-allied victory
| Dwight D. Eisenhower |
| Bay of Pigs Invasion (1961) Part of the Cold War Location: Cuba A4D-2 Skyhawks in flight over USS Essex during the Bay of Pigs Invasion in April 1961. | | | Cuban government victory
| John F. Kennedy |
| Dominican Civil War (1965–1966) Location: Dominican Republic US soldiers push a child underneath a Jeep to protect him during a firefight in Santo Domingo on May 5, 1965. |
| | US-allied victory
| Lyndon B. Johnson |
| Korean DMZ Conflict (1966–1969) Part of the Korean conflict and the Cold War Location: Korean Demilitarized Zone ROK and US troop stationed at the DMZ, 1967. | | | US-allied victory
| Lyndon B. Johnson (November 22, 1963 – January 20, 1969) Richard Nixon |
| Cambodian Civil War (1967–1975) Part of the Cold War Location: Cambodia US troops and tanks entering town in Cambodia. | Supported by:
| Supported by:
| Khmer Rouge-allied victory
| Lyndon B. Johnson (November 22, 1963 – January 20, 1969) Richard Nixon Gerald Ford |
| Multinational intervention in Lebanon (1982–1984) Location: Lebanon US Marines of the 32nd Marine Amphibious Unit come ashore to assume the management of the port of Beirut. | Multinational Force in Lebanon:
|
| Syrian-allied victory
| Jimmy Carter (January 20, 1977 – January 20, 1981) Ronald Reagan |
| United States invasion of Grenada (1983) Part of the Cold War Location: Grenada American soldiers in artillery positions at Grenada. | | Military advisors: List
| US-allied victory
| Ronald Reagan |
| Bombing of Libya (1986) Location: Libya USAF F-111 taking off for Libya | | | US victory
| |
| Tanker War (1987–1988) Location: Persian Gulf Iranian frigate Sahand after being attacked by U.S. aircraft. | | | US victory
| |
| United States invasion of Panama (1989–1990) Location: Panama U.S. troops prepare to take a neighborhood in Panama City, December 1989. | | | US-allied victory
| George H. W. Bush |
| Gulf War (1990–1991) Location: Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Israel M1 Abrams tanks of the 3rd Armored Division advance on Medina Ridge. | | | US-allied victory
| |
| Iraqi No-Fly Zone Enforcement Operations (1991–2003) Location: Iraq A Tomahawk cruise missile is fired from an Arleigh Burke-class destroyer during Operation Desert Fox in December 1998. | | | US-allied victory
| George H. W. Bush (January 20, 1989 – January 20, 1993) Bill Clinton George W. Bush |
| First U.S. Intervention in the Somali Civil War (1992–1995) Part of the Somali civil war (1991–present) Location: Somalia U.S. Marines on patrol in Somalia. | | | Somali victory / US-allied defeat
| George H. W. Bush (January 20, 1989 – January 20, 1993) Bill Clinton |
| Bosnian War and Croatian War (1992–1995) Part of the Yugoslav Wars Location: Bosnia and Herzegovina and Croatia A U.S. Army M-113 Armor Personnel Carrier prepares to pull an armored Humvee out of the mud in Bosnia and Herzegovina. | | | Inconclusive/Other Result
| |
| Intervention in Haiti (1994–1995) Location: Haiti U.S. Marine guarding an area in Haiti. | | | US-allied victory
| Bill Clinton |
| Kosovo War (1998–1999) Part of the Yugoslav Wars Location: Serbia A U.S. Air Force F-15E Strike Eagle takes off for an air strike mission. | | | US-allied victory [13] [14] [15] [16]
|
- ^ Advisory role from the forming of the MAAG in Vietnam to the Gulf of Tonkin incident.
- ^ Direct U.S. involvement ended in 1973 with the Paris Peace Accords. The Paris Peace Accords of January 1973 saw all U.S forces withdrawn; the Case–Church Amendment, passed by the U.S Congress on 15 August 1973, officially ended direct U.S military involvement .
- ^ The war reignited on December 13, 1974 with offensive operations by North Vietnam, leading to victory over South Vietnam in under two months.
21st-century wars
| Conflict | Allies | Belligerent | Result for the United States and its Allies | Presidents of the United States |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| War in Afghanistan (2001–2021) Part of the War on terror and the Afghanistan conflict Location: Afghanistan U.S. soldiers from A Company, 101st Airborne Division Special Troop Battalion air assault into a village inside Jowlzak valley in Afghanistan. | Formerly: |
Allied groups
Taliban splinter groups
2001 Invasion:
| Taliban victory / US-allied defeat
| George W. Bush (October 7, 2001 – January 20, 2009) Barack Obama Donald Trump Joe Biden |
| American intervention in Yemen (2002–present) Part of the War on terror, the Al-Qaeda insurgency in Yemen, the Yemeni Civil War and the Saudi Arabian-led intervention in Yemen Location: Yemen MQ-1 Predator commonly used in drone strikes in Yemen. |
Saudi-led coalition:
In support of:
|
| Ongoing
| George W. Bush (October 7, 2001 – January 20, 2009) Barack Obama Donald Trump Joe Biden |
| Iraq War (2003–2011) Part of the War on terror Location: Iraq U.S. soldiers at the Hands of Victory monument in Baghdad. | Post-invasion (2003–2011) List
Invasion phase (2003)
| Post-invasion (2003–2011)
Invasion phase (2003) | Inconclusive/Other Result
| George W. Bush (January 20, 2001 – January 20, 2009) Barack Obama |
| American intervention in the War in North-West Pakistan (2004–2018) Part of the War on terror and the War in North-West Pakistan Location: Pakistan MQ-1 Predator drones typically used in covert bombing operations in Pakistan. |
Supported by:
| | US-allied victory
| George W. Bush (January 20, 2001 – January 20, 2009) Barack Obama Donald Trump |
| Second U.S. Intervention in the Somali Civil War (2007–present) Part of the Somali Civil War, the Somali Civil War and the War on terror Location: Somalia and Northeastern Kenya U.S. Marines establish security positions at Baledogle Military Airfield in Somalia, December, 2020. |
Supported by:
Non-combat support:
|
| Ongoing
| George W. Bush (January 20, 2001 – January 20, 2009) Barack Obama Donald Trump Joe Biden |
| Operation Ocean Shield (2009–2016) Part of the War on terror Location: Indian Ocean A tall plume of black smoke rises from a destroyed pirate vessel that was struck by USSFarragut in March 2010. |
| Somali pirates | US-allied victory
| Barack Obama (January 20, 2009 – January 20, 2017) |
| International intervention in Libya (2011) Part of the Libyan Crisis and the First Libyan Civil War Location: Libya U.S. vessels launch missiles in support of Anti-Gaddafi rebels during the First Libyan Civil War. |
| | US-allied victory
| |
| Operation Observant Compass (2011–2017) Part of the War on terror and the Lord's Resistance Army insurgency Location: Uganda U.S. Marine Sgt. Joseph Bergeron, a task force combat engineer, explains combat marksmanship tactics to a group of Ugandan soldiers. | | | US-allied victory
| |
| American-led intervention in Iraq (2014–2021) Part of the Operation Inherent Resolve, the War in Iraq (2013–2017), the Spillover of the Syrian civil war, the War on terror and the International ISIS campaign Location: Iraq U.S. soldiers use a rooftop as an observation post, during the Battle of Mosul in Iraq, March, 2017. | | | US-allied Coalition and Iraqi victory
| Barack Obama (January 20, 2009 – January 20, 2017) Donald Trump Joe Biden |
| American-led intervention in Syria (2014–present) Part of the Operation Inherent Resolve, the Syrian civil war, the War on terror and the International ISIS campaign Location: Syria U.S. 1st Battalion, 6th Infantry Regiment troops conduct area reconnaissance patrol in Syria, February 2021. |
|
| Ongoing
| Barack Obama (January 20, 2009 – January 20, 2017) Donald Trump Joe Biden |
| American intervention in Libya (2015–2019) Part of the Operation Inherent Resolve, the Second Libyan Civil War, the War on terror, and the International ISIS Campaign Location: Libya USSWasp conducts flight operations in Operation Odyssey Lightning. |
| | ISIS in Libya largely defeated
| Barack Obama (January 20, 2009 – January 20, 2017) Donald Trump |
See also
- List of armed conflicts involving the United States
- Military history
- Timeline of United States military operations
- United States involvement in regime change
- List of ongoing armed conflicts
Notes
- ^ These numbers are gathered from a combination of surviving muster rolls and veteran applications for land grants. It is likely that the statistics on the Texan army size in both 1835 and 1836 underestimate the number of Tejanos who served in the army. American volunteers who returned to the U.S. without claiming land are also undercounted. Lack (1992), p. 113.
References
- ^ Kelly, Martin (November 4, 2020). "American Involvement in Wars From Colonial Times to the Present". ThoughtCo . Retrieved January 31, 2022.
- ^ a b c d e f "Tripolitan War | Encyclopedia.com". www.encyclopedia.com . Retrieved May 8, 2019.
- ^ a b r2WPadmin. "First Barbary War". American History Central . Retrieved May 8, 2019.
- ^ Serial 89, 18th Congress, 1st Session, Senate Document No. 1, p. 95
- ^ Lack (1992), pp. 122–3.
- ^ "The Indians". The Philadelphia Inquirer. November 12, 1884.
- ^ "Union and Confederate Indians in the Civil War". civilwarhome.com. February 16, 2002. Archived from the original on February 13, 2021. Retrieved December 12, 2021.
- ^ "City of Albuquerque". City of Albuquerque.
- ^ Yun, Jiwon (2019). "Vietnam's Politic of a Divided Nation: From the Reunification to DoiMoi (Renovation) and Its Implication for the Korean Peninsula and North Korea". International Journal of Korean Unification Studies. 28 (1): 63–92. doi:10.33728/ijkus.2019.28.1.003 . Retrieved September 24, 2020.
- ^ "Who won the Vietnam War? | Britannica". www.britannica.com . Retrieved June 4, 2022.
- ^ "Statement by Deputy Press Secretary Larry Speakes". September 23, 1982.
- ^ Brinkley, Joel (March 11, 1984). "The Collapse of Lebanon's Army: U.S. Said to Ignore Factionalism". The New York Times.
- ^ Article title[ bare URL PDF ]
- ^ Cambridge Scholars Publisher (2015). Coercive Diplomacy of NATO in Kosovo. Cambridge Scholars Publishing. pp. 289–. ISBN978-1-4438-7668-1.
- ^ Erlanger, Steven (November 7, 1999). "NATO Was Closer to Ground War in Kosovo Than Is Widely Realized". The New York Times.
- ^ Lake, Daniel R. (2009). "The Limits of Coercive Airpower: NATO's "Victory" in Kosovo Revisited". International Security. 34: 83–112. doi:10.1162/isec.2009.34.1.83. S2CID 57572298.
- ^ "Central Asian groups split over leadership of global jihad". The Long War Journal. August 24, 2015. Retrieved August 27, 2015.
- ^ "U.S. Troops in Afghanistan now down to 2,500, lowest since 2001: Pentagon". Reuters. January 15, 2021.
- ^ "Remarks by President Biden on Afghanistan". The White House. August 16, 2021.
- ^ Gibbons-Neff, Thomas; Katzenberg, Lauren (August 30, 2021). "The U.S. military finishes its evacuation, and an era ends in Afghanistan". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved August 30, 2021.
- ^ Lou, Mary (January 1, 2022). "Taliban a 'major U.S. arms dealer' after weaponry left behind in Afghanistan, watchdog warns". Just The News. Retrieved August 15, 2022.
- ^ "Drone War: Yemen". The Bureau of Investigative Journalism. Retrieved June 28, 2019.
- ^ "Yemen Leaders Killed". Washington, DC, USA: New America. Retrieved April 20, 2018.
- ^ "The War in Yemen". newamerica.org . Retrieved December 9, 2021.
- ^ Gatehouse, Gabriel (September 11, 2015). "Inside Yemen's forgotten war". BBC News. Archived from the original on October 29, 2015.
- ^ "Sectarian divisions change Baghdad's image". NBC News. July 3, 2006. Retrieved February 18, 2007.
- ^ Petrou, Michael (September 9, 2011). "The decline of al-Qaeda". Maclean's.
George W. Bush gambled on surging thousands more troops to the embattled country. It paid off. Al-Qaeda in Iraq is now a diminished force without territory.
- ^ Spencer C. Tucker (December 14, 2015). U.S. Conflicts in the 21st Century: Afghanistan War, Iraq War, and the War on Terror. ISBN978-1-4408-3879-8.
Al Qaeda in Iraq was decimated by the end of the Iraq War in 2011
- ^ South, Todd (January 20, 2019). "Army's long-awaited Iraq war study finds Iran was the only winner in a conflict that holds many lessons for future wars". Army Times . Retrieved January 20, 2019.
- ^ Galbraith, Peter W. (2007). The End of Iraq: How American Incompetence Created a War Without End. Simon & Schuster. p. 74. ISBN978-0-7432-9424-9.
- ^ "Iran expands regional 'empire' ahead of nuclear deal". Reuters. March 23, 2015.
- ^ "How to Stop Iran's Growing Hegemony". National Review Online. April 10, 2015.
- ^ "The JRTN Movement and Iraq's Next Insurgency | Combating Terrorism Center at West Point". Ctc.usma.edu. Archived from the original on August 26, 2011. Retrieved August 2, 2014.
- ^ "Al-Qaeda's Resurgence in Iraq: A Threat to U.S. Interests". U.S. Department of State. February 5, 2014. Retrieved November 26, 2010.
- ^ "Drone War: Pakistan". The Bureau of Investigative Journalism. Retrieved April 20, 2018.
- ^ "Pakistan Leaders Killed" Archived 18 September 2017 at the Wayback Machine. New America Foundation. 23 June 2018
- ^ "US Drone Kills Afghan-Based Pakistani Taliban Commander". Voice of America (VOA). July 4, 2018.
- ^ "CIA drone strikes in Pakistan, 2004 to present". Bureau of Investigative Journalism. 24 January 2018. Archived from the original on 5 March 2017. Retrieved 15 March 2019.
- ^ Somalia, EUTM. "Home". EUTM-Somalia . Retrieved April 18, 2019.
- ^ a b c "Service and Sacrifice: Ugandan 'Blue Helmets' support UN efforts to bring peace to Somalia". UN News. April 18, 2019. Retrieved April 18, 2019.
- ^ "Somali, U.S. forces engage insurgents in support of the Federal Government of Somalia". www.africom.mil. February 23, 2022.
- ^ "Biden approves deployment of hundreds of US troops to Somalia". aljazeera.com. June 4, 2022.
- ^ "New Somali President Welcomes Return of US Troops". voanews.com. June 4, 2022.
- ^ "Somali piracy is down 90 per cent from last year". The Journal. December 15, 2013. Retrieved January 14, 2014.
- ^ Holmes, Oliver (January 24, 2012). "UPDATE 1-Anger, chaos but no revolt after Libya violence". Bani Walid. Reuters Africa. Archived from the original on April 30, 2012. Retrieved January 24, 2012.
- ^ "Baghdad declares victory over ISIS". NBC News. February 5, 2018. Retrieved March 3, 2019.
- ^ "IS left 200 mass graves in Iraq - UN". November 6, 2018. Retrieved June 21, 2019.
- ^ Arraf, Jane (December 9, 2021). "U.S. Announces End to Combat Mission in Iraq, but Troops Will Not Leave". The New York Times. Archived from the original on December 28, 2021.
- ^ "US-led combat mission in Iraq ends, shifting to advisory role". aljazeera.com.
- ^ "U.S.-led troops end Iraq combat mission, as planned - military officials". reuters.com. December 9, 2021.
- ^ Reuters (June 15, 2019). "Belgium takes back six children of Isis fighters from Syrian camps". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved June 15, 2019.
- ^ Seligman, Lara. "Troops to stay put in Syria even as Biden seeks to end America's 'forever wars'". Politico. Politico. Retrieved March 13, 2022.
External links
- Heidelberg Institute for International Conflict Research (HIIK)
- Conflict Barometer – Describes recent trends in conflict development, escalations, and settlements
- A Continent Divided: The U.S.-Mexico War [ permanent dead link ] , Center for Greater Southwestern Studies, the University of Texas at Arlington
- Timeline of wars involving the United States, Histropedia
- U.S. Periods of War and Dates of Recent Conflicts, Congressional Research Service
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_wars_involving_the_United_States

























































































0 Response to "Continual Us Involvement in Armed Conflicts"
Post a Comment